What is the economic value of energy in a society? This is a question so complex in reach and implication that organizations across the globe devote entire conferences, publications and funded research to explore and interpret the answers. The economic impacts of energy production cannot go unnoticed.
The most basic conclusion of these efforts is that affordable and reliable energy is the key pillar of economic stability. Energy has been labeled as the very lifeblood or oxygen of an economy and critical to human well-being. The dichotomous challenge is to balance increased consumption with technological evolution that preserves the environment and the well-being of humanity.
Which of the following are possible economic impacts of increased energy production?
- Job creation (14%)
- Increased tax revenues (9%)
- Royalty payments for property owner. (6%)
- All of the above (61%) [CORRECT]
- None of the above (9%)
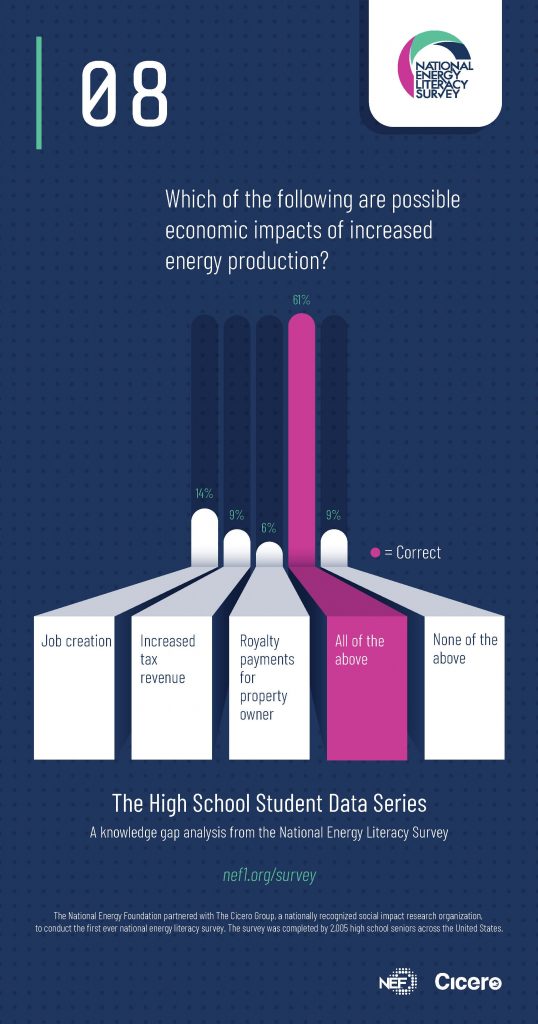
Participants in the national survey were cognizant of this connection as was evident by their answers to the question concerning the possible economic impacts of increased energy production. Over sixty percent answered correctly that the impacts include a variety of economic benefits. Another twenty-nine percent recognized that there existed a benefit in at least one area. Less than ten percent of students failed to understand this intricate connection between energy and the economy.
Three Economic Impacts of Energy Production
The energy sector is driving job growth. According to the 2018 U.S. Energy and Employment Report the traditional energy sector (made up of fuels production and generation, transmission and distribution) saw an increase of about 133,000 new jobs in 2017. The energy efficiency sector (responsible for the design, installation and manufacture of energy efficient products) added another 67,000 jobs. Wind, gas and storage jobs all increased in 2017 as well.
Revenues to federal, state and local communities are all increased by the extraction and production of energy. Companies pay a wide range of fees, rates, royalties and taxes to extract natural resources in the U.S. The Department of the Interior (DOI) indicates that the amounts differ depending on the ownership of the resources and are called revenue because they represent a financial benefit to the American public. Several federal agencies as well as private land owners receive the paid fees, benefiting from the direct economic impacts of energy production.
Royalties, a percentage of the sales value of extracted resources can reach as high as 18.75% but vary depending on location and statutes. These fees make up most of the revenue paid to DOI and are a direct benefit to private individuals.
Corporations operating the extractive and production industries also pay taxes to the IRS on their income. These income tax rates range from 15-35%, but might be influences by tax credits to incentivize production of specific resources, specifically domestic and renewable resources.
Job creation in the energy sector, royalties and increased tax revenues are all major players in the economic impacts of energy production.
Technology Advancements in Energy Impact the Economy
In addition to the financial benefits listed above, one cannot overstate the economic impact of technological advancements in the energy sector. Demonstrated, specifically, in the first two decades of the 2000s by the combining of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing. In 2008, with the U.S. in a deep economic recession, importing approximately 50% of its petroleum and natural gas prices on the rise, many were forecasting an energy crisis on top of the current economic crises.
But the new technologies for extracting oil and gas marked the fastest oil and gas production increase in U.S. history. This dramatic shift is greatly responsible for turning the economy of the U.S. It created an economic windfall in transportation, manufacturing, exporting commodities, jobs and eventually the markets. In this case, economic impacts of energy production was paramount. This overabundance of natural gas also contributed to the lowering of carbon emissions and environmental improvements; working to create a needed balance in the well-being of U.S. communities.
__
During the 2016-2017 school year, NEF launched an unprecedented initiative call the National Energy Literacy Survey. The energy survey measured high school students’ knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors. For more information regarding the National Energy Literacy Survey please reach out to [email protected]


